Resizing or modifying a VM with a UMI fails via Azure PowerShell/CLI but succeeds in Azure Portal
Overview
When performing certain operations on an Azure VM or VMSS - such as resizing or changing VMSS image reference - if you assigned a User Assigned Managed Identity to the VM/VMSS, you may encounter failures when using Azure PowerShell or Azure CLI. However, performing the same operation through the Azure portal succeeds. This blog post explains the root cause and provides guidance on how to resolve the issue.
Issue Description
Symptoms
You have assigned a User Assigned Managed Identity to the Azure VM.
You have limited access or use a custom RBAC role.
When attempting operations such as resizing the VM or modifying the VMSS using Azure PowerShell or Azure CLI, the process fails.
Typical Error Message (Azure PowerShell Example):
Update-AzVM : The client 'username@domain' with object id '00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000' has permission to perform action 'Microsoft.Compute/virtualMachines/write' on scope '/subscriptions/<subid>/resourceGroups/<rg>/providers/Microsoft.Compute/virtualMachines/<vmname>'; however, it does not have permission to perform action(s) 'Microsoft.ManagedIdentity/userAssignedIdentities/assign/action' on the linked scope(s) '/subscriptions/<subid>/resourceGroups/<rg>/providers/Microsoft.ManagedIdentity/userAssignedIdentities/<uminame> (respectively) or the linked scope(s) are invalid. ErrorCode: LinkedAuthorizationFailed ErrorTarget: StatusCode: 403 ReasonPhrase: Forbidden OperationID : 00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000Portal Succeeds: When performing the same operation through the Azure Portal, it completes without any issues.
Root Cause Analysis
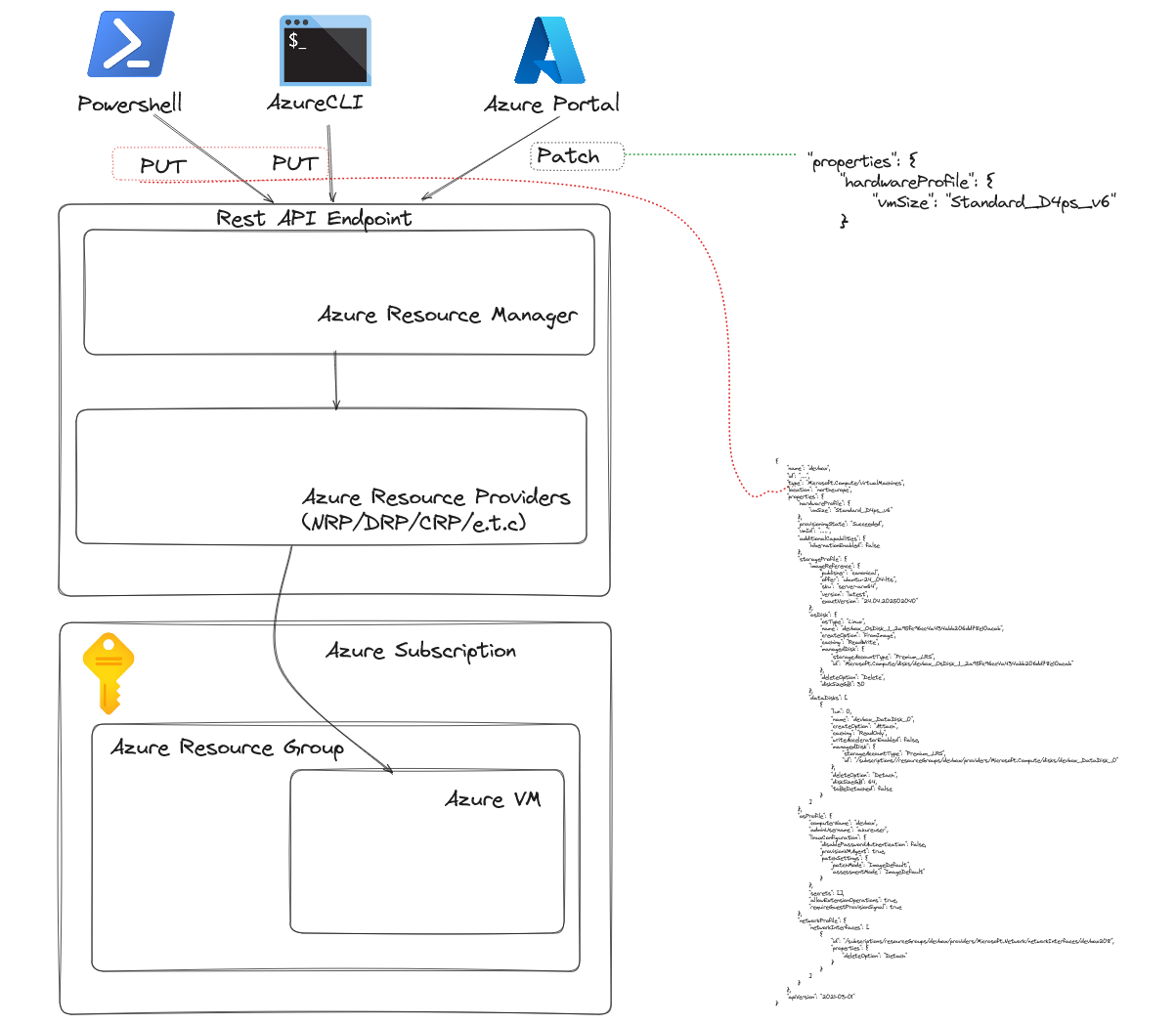
Azure’s resource management operations - whether executed via Azure Portal, PowerShell, or CLI - ultimately translate into REST API calls. However, the type of call and the validation performed can differ based on the tool:
- Azure Portal → PATCH Operation
- When you resize (or modify) a VM in the Azure Portal, it typically issues a
PATCHcall. APATCHcall updates only the specific part of the VM schema (e.g., the hardware profile for changing VM size). Hence, only the VM size change is validated, and no validation is performed on the entire schema, including the UMI.
- When you resize (or modify) a VM in the Azure Portal, it typically issues a
- Azure PowerShell/CLI → PUT Operation
- When performing the same operation using Azure PowerShell or CLI, a
PUTcall is made. APUTcall attempts to update the entire VM schema. This requires validation of all attached resources, including the UMI. If the user lacks the required permission on the UMI resource- specifically theMicrosoft.ManagedIdentity/userAssignedIdentities/assign/actionpermission—the operation fails with aLinkedAuthorizationFailederror.
- When performing the same operation using Azure PowerShell or CLI, a
In other words, the reason the operation fails via Azure PowerShell/CLI but succeeds through the Portal is that the Portal-based PATCH approach does not re-validate every property (including the UMI), while PowerShell/CLI’s PUT approach does.
Resolution
- Grant Proper Permissions
- Ensure the user account performing the action has the necessary RBAC permissions on the User Assigned Managed Identity resource.
- Specifically, grant the Managed Identity Contributor role or a custom role that includes the permission
Microsoft.ManagedIdentity/userAssignedIdentities/assign/action. - For guidance:
- Use the Azure Portal
- If adjusting permissions is not immediately feasible, an alternative short-term workaround is to perform the VM or VMSS operation through the Azure Portal, which issues a
PATCHoperation rather thanPUT. This avoids the comprehensive re-validation that triggers the permission error.
- If adjusting permissions is not immediately feasible, an alternative short-term workaround is to perform the VM or VMSS operation through the Azure Portal, which issues a
- Call the Azure REST API Directly
In advanced scenarios, you can bypass the typical PowerShell/CLI
PUTby constructing your own API calls that only apply aPATCH. This is more complex and usually not necessary if you can assign the correct permissions or use the portal.There are two ways to do it, one is to use Azure CLI: Use the Azure REST API with Azure CLI | Microsoft Learn
Second one is bypassing AzureCLI and using custom Power Shell code, calling Invoke-RestMethod. Example below:
# Get your access token via # az account get-access-token --query 'accessToken' -o tsv $headers = @{ "Authorization" = "Bearer YOURACCESSTOKEN" "Content-Type" = "application/json" } # Replace with your subscribtion IDs and VMss $subscriptionId = "YOURSUBID" $resourceGroupName = "testvmss" $vmssName = "testvmss" # Replace with yours ID $imageReferenceId = "/subscriptions/$subscriptionId/resourceGroups/testimage/providers/Microsoft.Compute/galleries/testgallery/images/test/versions/0.0.1" # Update VMSS Image Reference - JSON payload $jsonBody = @" { "properties": { "virtualMachineProfile": { "storageProfile": { "imageReference": { "id": "$imageReferenceId" } } } } } "@ $uri = "https://management.azure.com/subscriptions/$subscriptionId/resourceGroups/$resourceGroupName/providers/Microsoft.Compute/virtualMachineScaleSets/$vmssName`?api-version=2022-11-01" Invoke-RestMethod -Uri $uri -Method Patch -Headers $headers -Body $jsonBody
Additional Resources
- Azure REST API reference documentation | Microsoft Learn
- Azure RBAC documentation | Microsoft Learn
- RESTful web API design | Microsoft Learn - Put vs Patch