Azure Capacity Reservations and Azure Reserved Instances
Azure Capacity Reservation Overview
Microsoft Azure offers various solutions that help you to optimize cloud operations efficiency: Azure Reservations and Reserved Instances. While both have “Reserve” keyword in their name they serve different purposes. Let’s take a look into what Azure Capacity Reservations are, how they differ from Azure Reserved Instances, and when you should consider using them.
Azure Reserved Instances
Azure Reserved Instances allow you to commit to a specific amount of resources for a defined period (one or three years), in return for a discounted rate. For instance, if you commit to using a certain type of virtual machine for one year, Azure offers you a huge discount. Committing for three years increases the discount even further. The main point to note here is that while you get cost savings, Azure Reserved Instances do not guarantee that the reserved capacity will be available when you need it.
On-demand Capacity Reservations
The need for a more secure, guaranteed availability brings us to Capacity Reservations. These reservations ensure that a specific type of virtual machine in a specific region or even availability zone is set aside for you. Once you pay, this capacity becomes guaranteed, backed by a Service Level Agreement. This setup is particularly useful for mission-critical applications or during times when you anticipate a significant deployment and want to ensure there are no capacity issues.
Features of Capacity Reservations
- Region Specific: You can tie the reservation to a particular region, such as North Europe.
- AZ Specific: If the region supports availability zones, you can specify which AZ the capacity reservation applies to.
- VM Type: You specify an exact VM size, not just a family of VMs.
- Flexible Duration: Unlike Azure Reservations, Capacity Reservations don’t have a fixed duration. You can create and cancel them at any time, but you will be billed for the time the reservation exists.
- Dynamic Adjustment: You can dynamically change the number of reserved instances within your capacity reservation group, offering greater flexibility.
How to Create a Capacity Reservation
Creating a Capacity Reservation involves two main steps:
Create a Capacity Reservation Group: This is essentially a container that holds your capacity reservations. The group is specific to a region, and optionally, an availability zone.
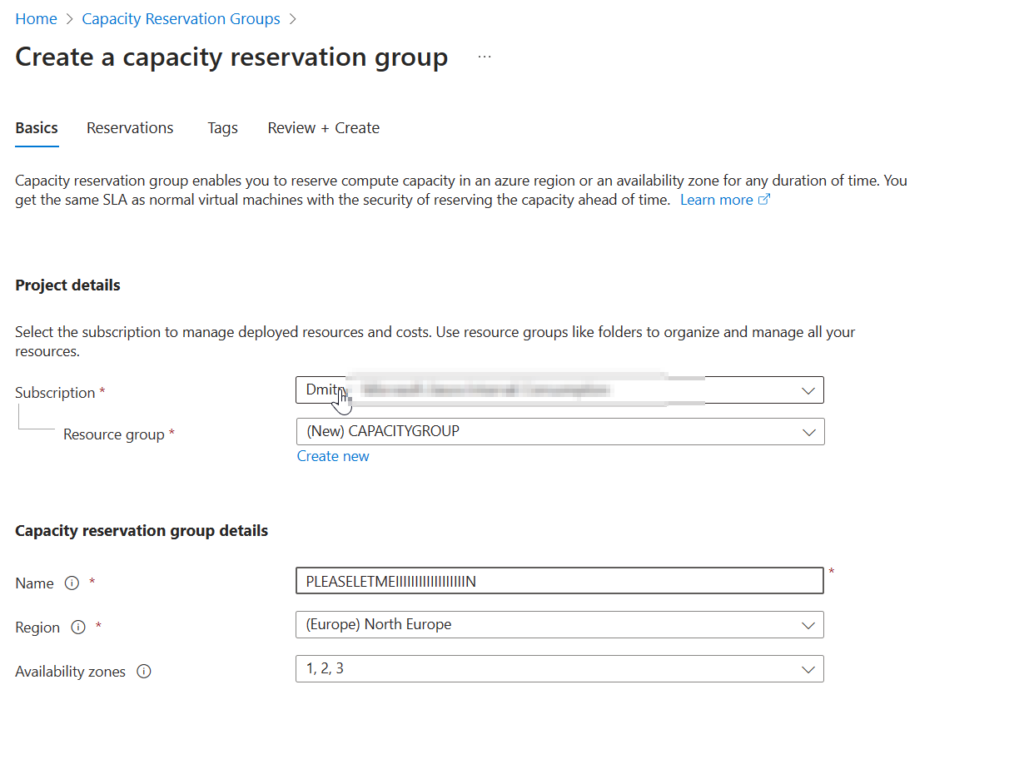
Create Individual Reservations: Within this group, you create one or more reservations by selecting the exact VM size you need.
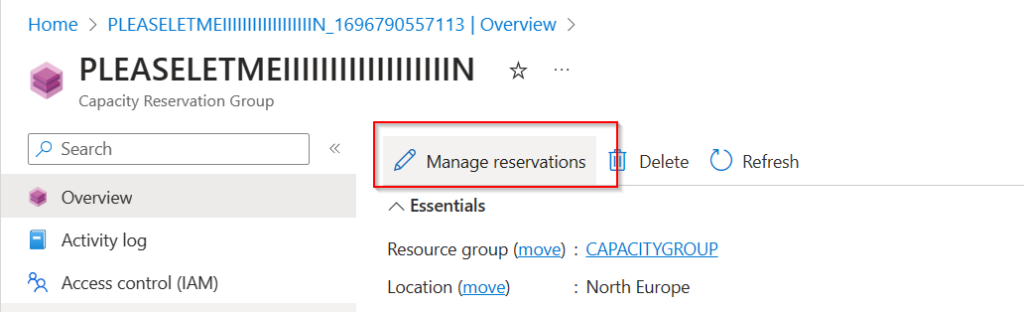
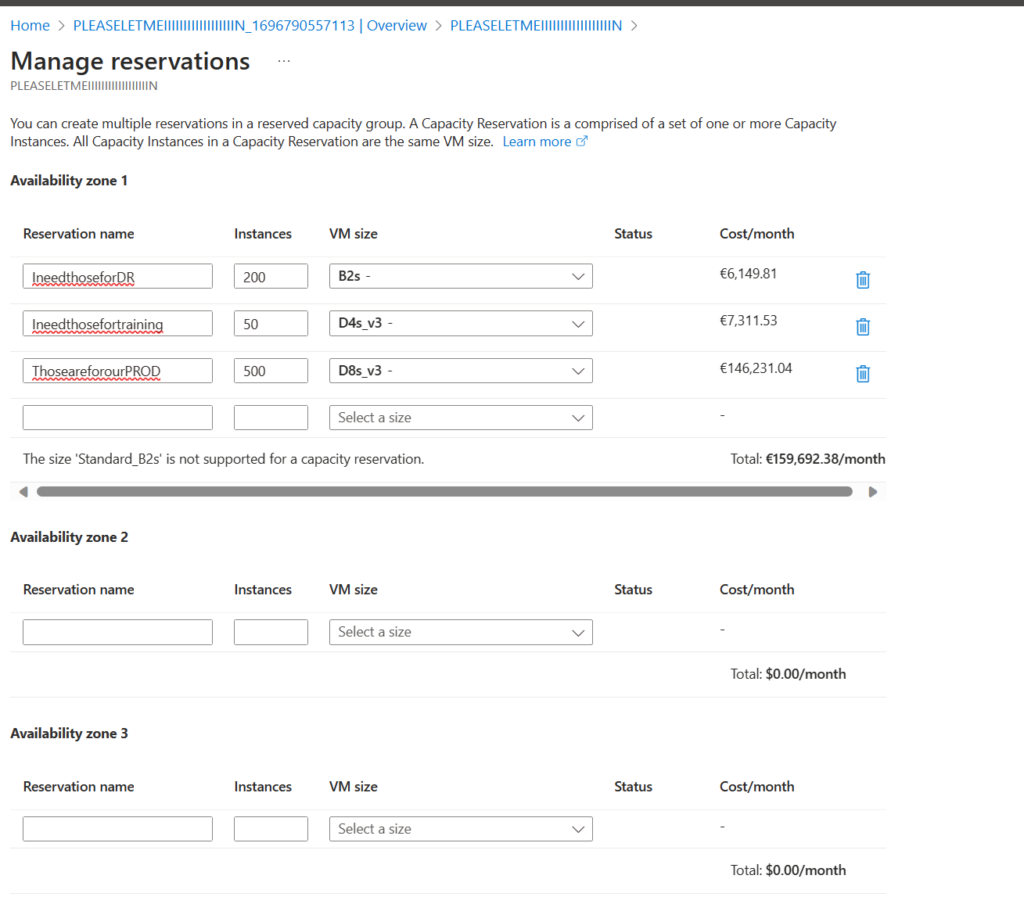
Once these steps are complete, Azure will check for the availability and quota in your subscription. If all checks pass, your reservation becomes active, and billing starts.
Use Cases for Capacity Reservations
- Guaranteed Deployments: If you have a significant rollout planned, perhaps over the weekend, using Capacity Reservations ensures your resources are available.
- Disaster Recovery: In case of an unexpected event causing failure in one region, having capacity reservations in another region ensures that your critical workloads can be moved and started immediately, for example if you are using Azure Site Recovery.
- SLA-backed Assurance: For applications where uptime and availability are non-negotiable, Capacity Reservations offer peace of mind.
While Azure generally offers sufficient capacity, there are scenarios where the additional assurance of Capacity Reservations can be invaluable, for example during DR scenarios.