Intro
This guide gives a step-by-step walkthrough for configuring a site-to-site IKEv2 IPsec VPN tunnel on a MikroTik RouterOS device. This was tested on RouterOS 7.20.
If you follow instructions below, you will establish a secure, encrypted connection between your local network and a remote gateway (Harmony SASE in this exapmple).
Sample Harmony SASE configuration below
(it is a default config, when creating a tunnel). If you will change default configuration, you’ll have to adjust parameters in RouterOS commands as well.
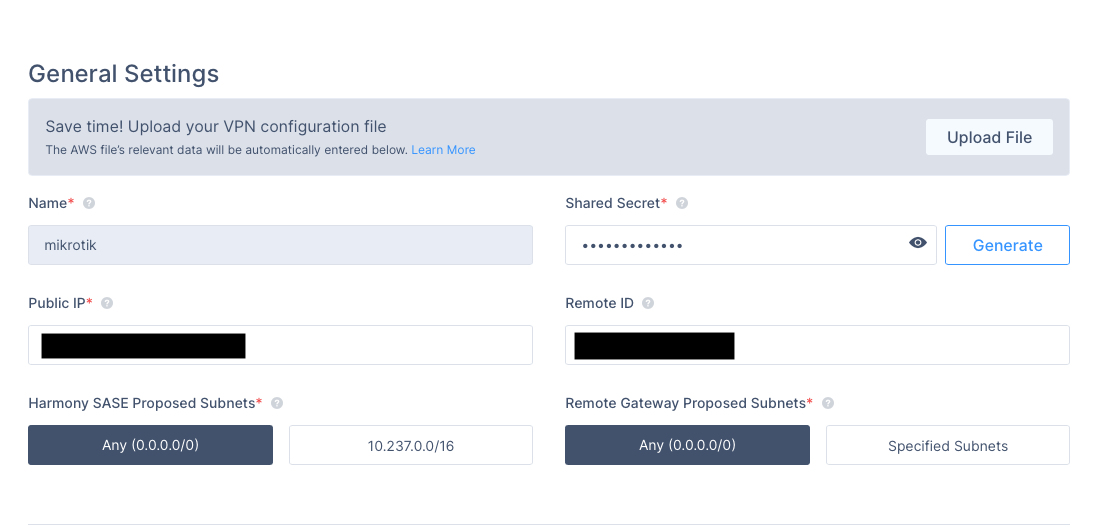
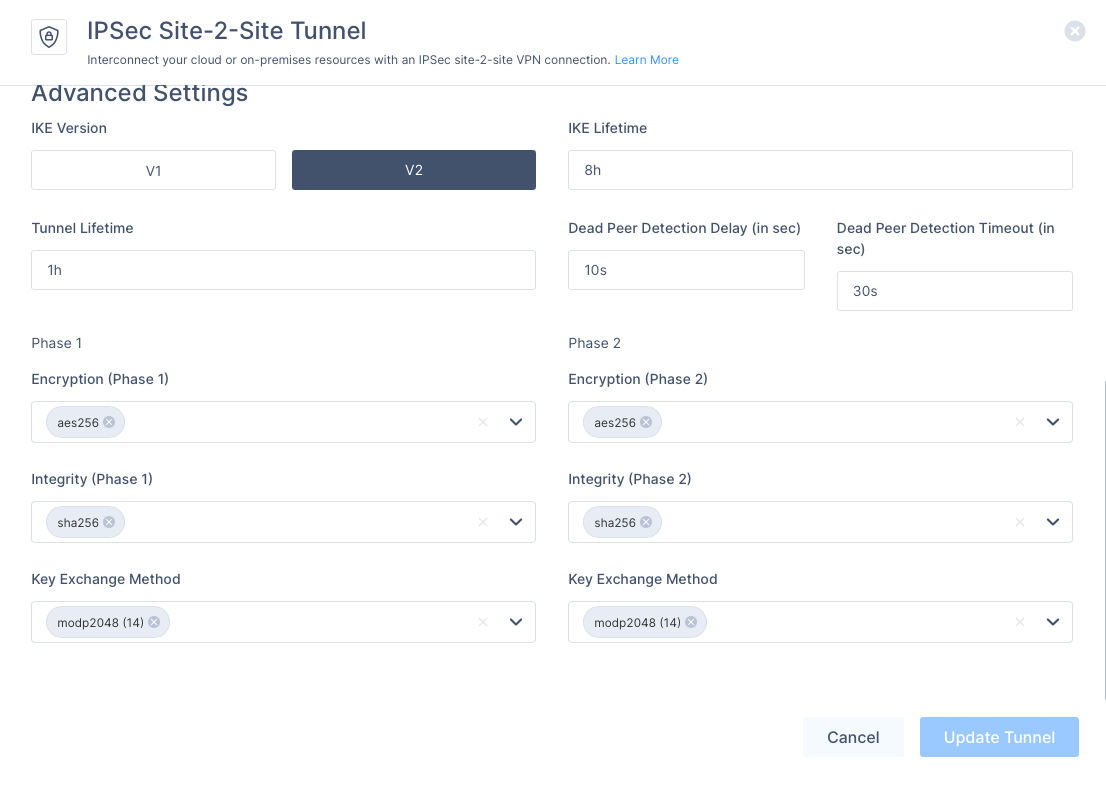
On Mikrotik side
Create Phase 1 (IKEv2) profile
/ip ipsec profile add name=harmony-ike2 enc-algorithm=aes-256 hash-algorithm=sha256 dh-group=modp2048 lifetime=8h dpd-interval=10s dpd-maximum-failures=3
Create the peer (remote gateway). You must bind it to local router WAN IP (B) as the IP should exist in Mikrotik.
/ip ipsec peer
add name=harmony-peer address=<HARMONYGWIP>/32 exchange-mode=ike2 local-address=<LOCALWANIP> profile=harmony-ike2 send-initial-contact=yes
(Optional, if your router WAN IP and real public IP mimatch) B. Bind peer to router WAN IP:
/ip ipsec peer
set [find name="harmony-peer"] local-address=<ROUTER WAN IP>
Add identity (PSK + IDs)
/ip ipsec identity add peer=harmony-peer auth-method=pre-shared-key secret="<YOURPSKSECRET>" my-id=address:<MICROTIKPUBLICIP>
Create Phase 2 (ESP) proposal
/ip ipsec proposal
add name=harmony-p2 enc-algorithms=aes-256-cbc auth-algorithms=sha256 pfs-group=modp2048 lifetime=1h
Create traffic selectors (Pick A or B depending on your needs)
A. Split tunnel:
/ip ipsec policy
add src-address=<LANNET> dst-address=<REMOTE_NET> tunnel=yes peer=harmony-peer proposal=harmony-p2
B. Full tunnel (0.0.0.0)
/ip ipsec policy
add src-address=<LANRANGE> dst-address=0.0.0.0/0 tunnel=yes peer=harmony-peer proposal=harmony-p2
Extra configuration steps
do NAT bypass if you have masquerade rule
/ip firewall nat add chain=srcnat action=accept src-address=<LOCAL_LAN> dst-address=<REMOTE_NET>
Allow IPsec on WAN interface
/ip firewall filter
add chain=input action=accept protocol=udp dst-port=500,4500 in-interface=ether1 comment="Allow IKE/IPsec NAT-T"
add chain=input action=accept protocol=ipsec-esp in-interface=ether1 comment="Allow ESP"
Allow IPSec in forward
/ip firewall filter
add chain=forward action=accept ipsec-policy=in,ipsec comment="Allow IPsec in"
add chain=forward action=accept ipsec-policy=out,ipsec comment="Allow IPsec out"
Verify configuration
/ip ipsec active-peers print
/ip ipsec installed-sa print
If everything works, you should see something like this:
[[email protected]] /ip/firewall/filter> /ip ipsec active-peers print
Flags: N - NATT-PEER
Columns: ID, STATE, UPTIME, PH2-TOTAL, REMOTE-ADDRESS
# ID STATE UPTIME PH2-TOTAL REMOTE-ADDRESS
0 N <REMOTEIP> established 22m56s 1 <REMOTEIP>
[[email protected]] /ip/firewall/filter> /ip ipsec installed-sa print
Flags: S - SEEN-TRAFFIC; H - HW-AEAD; E - ESP
Columns: SPI, STATE, SRC-ADDRESS, DST-ADDRESS, AUTH-ALGORITHM, ENC-ALGORITHM, ENC-KEY-SIZE
# SPI STATE SRC-ADDRESS DST-ADDRESS AUTH-ALGORITHM ENC-ALGORITHM ENC-KEY-SIZE
0 SHE 0x9965D31 mature <REMOTEIP>:4500 <LOCALIP>:4500 sha256 aes-cbc 256
1 SHE 0xCEFCCEC4 mature <LOCALIP>:4500 <REMOTEIP>:4500 sha256 aes-cbc 256
Troubleshooting
View logs
/log print where topics~"ipsec"
Check ipsec traffic
/tool sniffer quick ip-address=<REMOTEIP> port=4500
Enable extra logging
/system logging add topics=ipsec,debug action=memory
View IPSEC logs
/log print where topics~"ipsec"
Remove extra logging
/system logging remove [find where topics="ipsec,debug" and action=memory]